Automated Budget System In State Governance
An enterprise solution that offers improved transparency and accountability in the budget and expenditure management process.
Role
Research
Information Architecture
Platform
Desktop
Mobile Responsive
Summary
Nigeria's budget challenges and potential reforms: Nigeria faces significant challenges in managing its budget effectively, leading to inefficiencies and hindrances in economic growth and development.

Tackling Financial Data Issue
Outdated & Decentralized Data
Civil servants grapple with outdated financial data and decentralized information across government departments, contributing to a lack of transparency and accountability.
These issues are further compounded by corruption, inadequate revenue, and high expenses, resulting in a substantial budget deficit of ₦5.60 trillion in 2021.
To address these challenges, the World Bank is sponsoring projects aimed at promoting transparency and accountability within state governance.
This external support underscores the international recognition of the importance of tackling these issues for Nigeria's development. The collaboration with the World Bank brings additional resources and expertise to the table, facilitating the implementation of reforms and strengthening the country's capacity to manage its budget effectively.
Design Process
Comprehensive Research Unveils Budget Process Dynamics: Insights & Personas Revealed
To address the challenges at hand, I designed an enterprise-level solution aimed at enhancing transparency and accountability in budget and expenditure management processes.
My approach began with a comprehensive series of interviews to grasp the intricacies of user workflows. These interviews provided insights into user interactions, tasks, emotions, and timeframes involved in their processes. Through meticulous data collection and analysis, I identified key user roles and constructed an informative process flowchart illustrating their interactions and workflows.
Quick stats
2
States
53
Participants
23
MDAs
5.5
Weeks
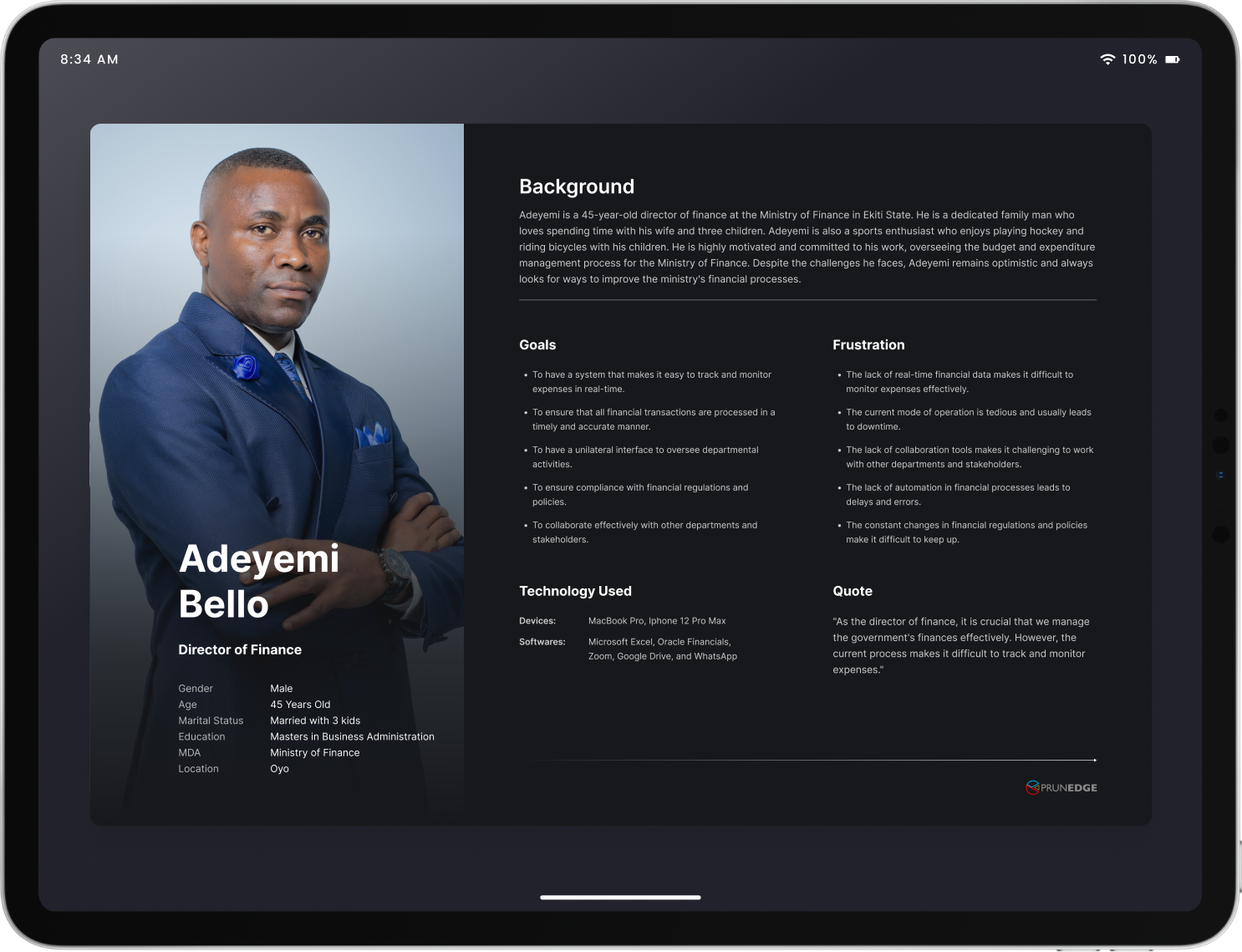
User persona
Features
During the ideation stage, we generated potential features and ideas for the budget and expenditure module. This list is not exhaustive.

What we uncovered
Additionally, field surveys were conducted across two states to further refine our understanding and identify potential user personas:
Expanding the Actors
Recognizing the diverse responsibilities within the actor role, we subdivided users to ensure system flexibility:
What’s included
- Initiators
- Authors
- Directors
- Supervisor Officers
- Accounting Officers
Output
This meticulous approach not only provided insights into budget implementation and expenditure initiation but also ensured the system's adaptability to varied user roles and responsibilities.
Moving into design
Pivoting to using a timeline approach to manage their activities
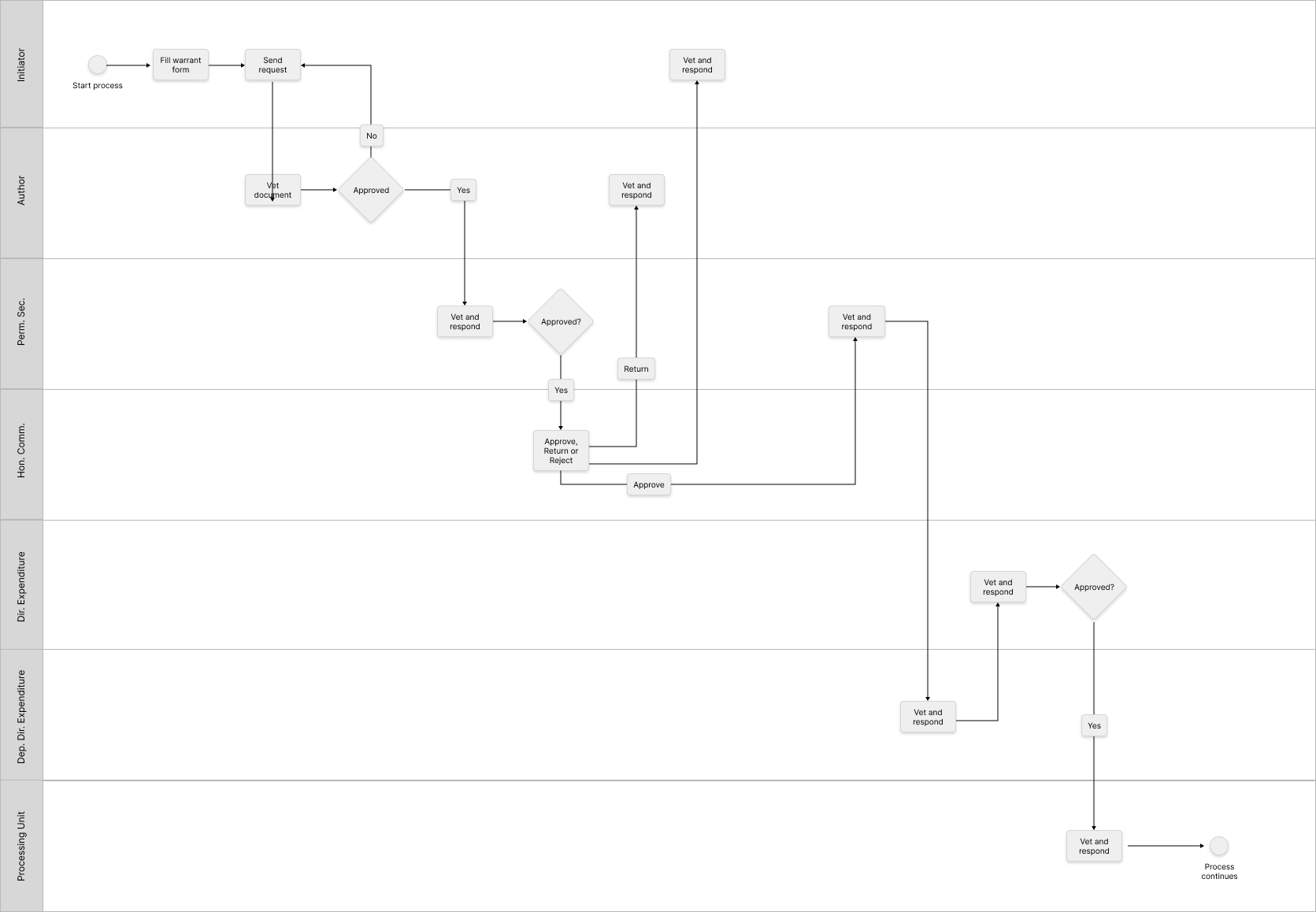
Having explored series of UI designs, starting from wireframes with the technical team to creating hi-fidelity for the larger stakeholder, we pivoted to using A-Timeline approach for managing their day-to-day activities.
Due to the needed flexibility within each departments, I created process management tool, where users with the right access can specifiy the flow of certain tasks using some parameter
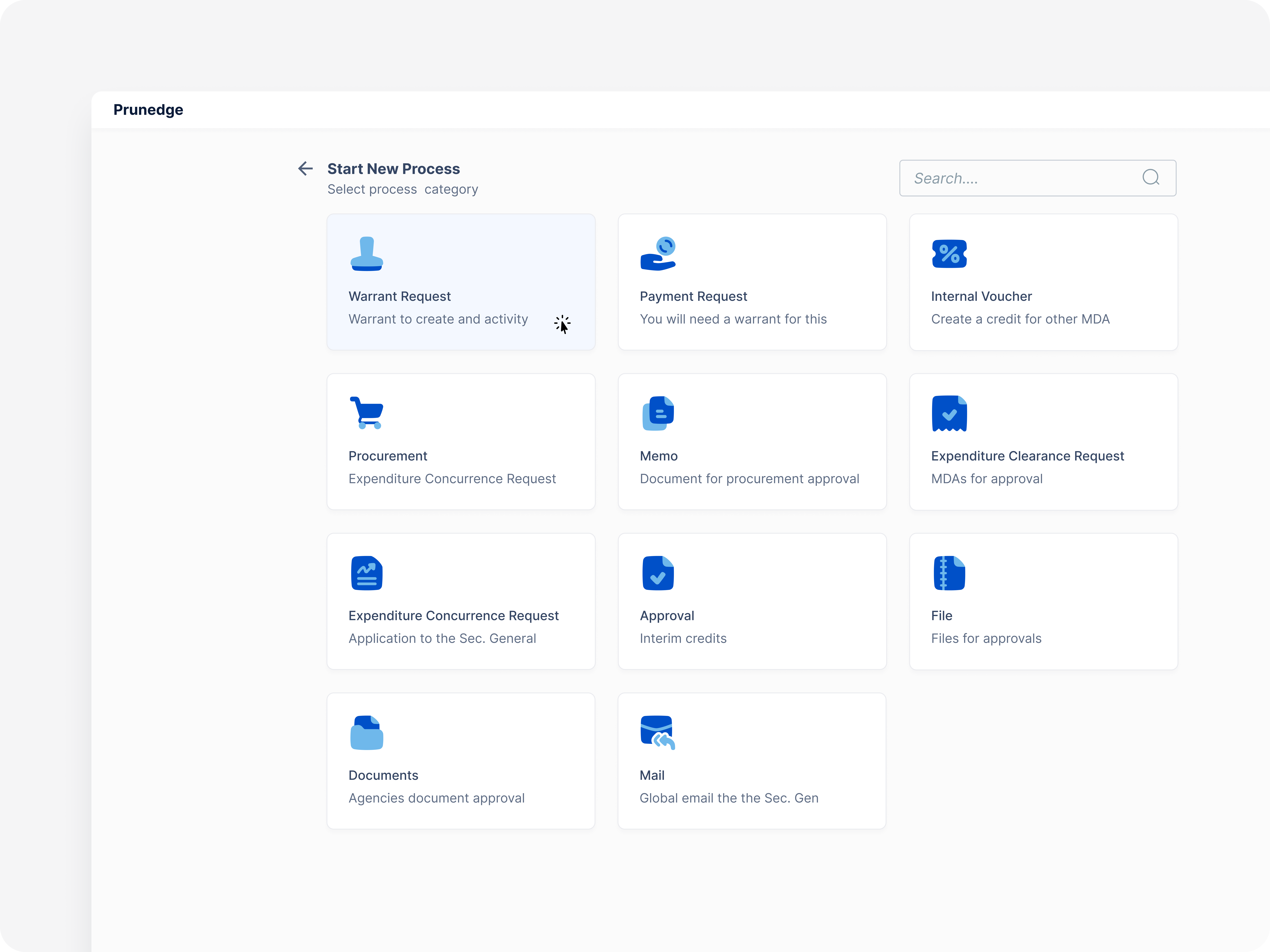
Starting A Process
Process by an officer to balance the state ledger and bank statement of account for the state.
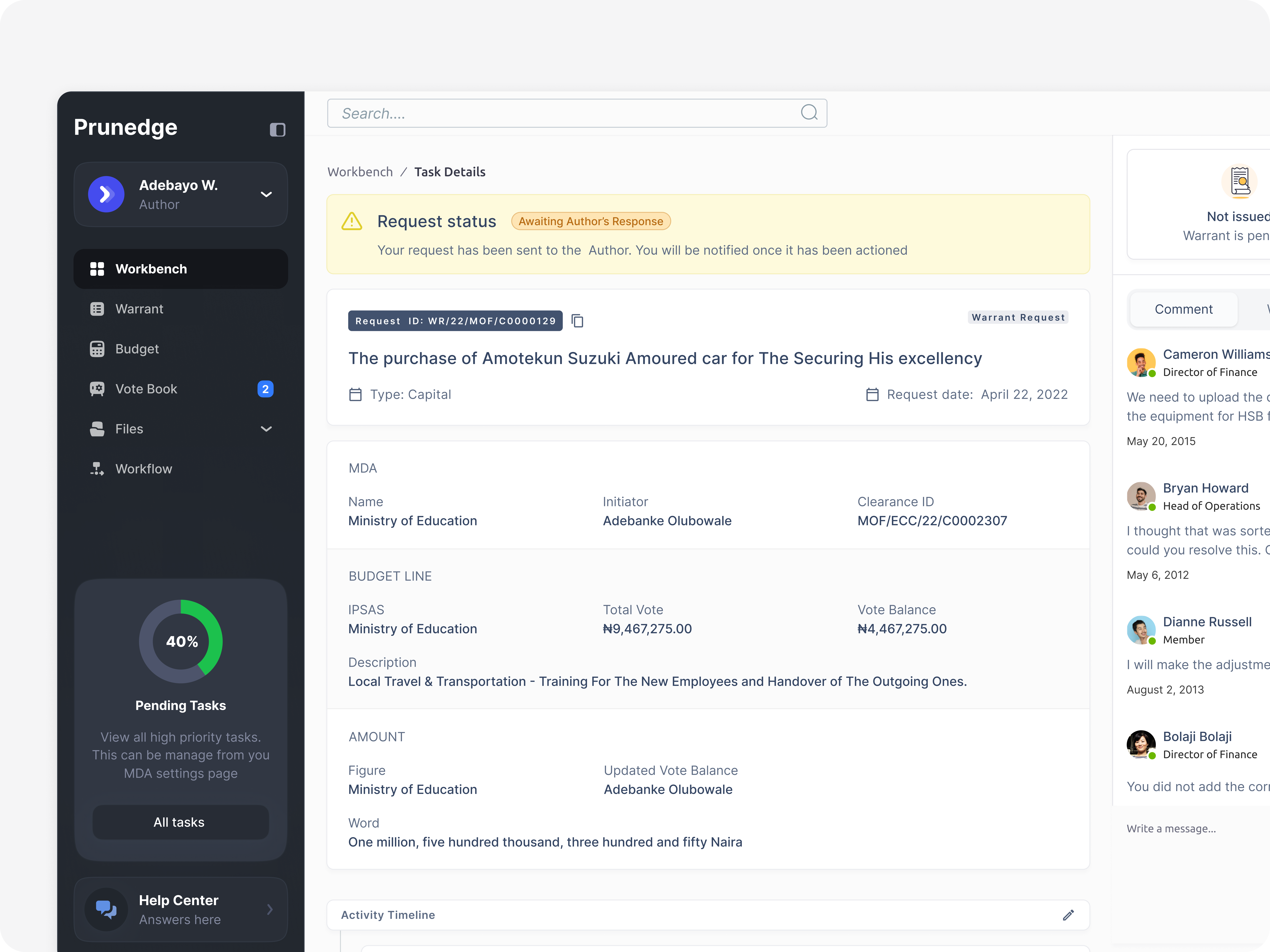
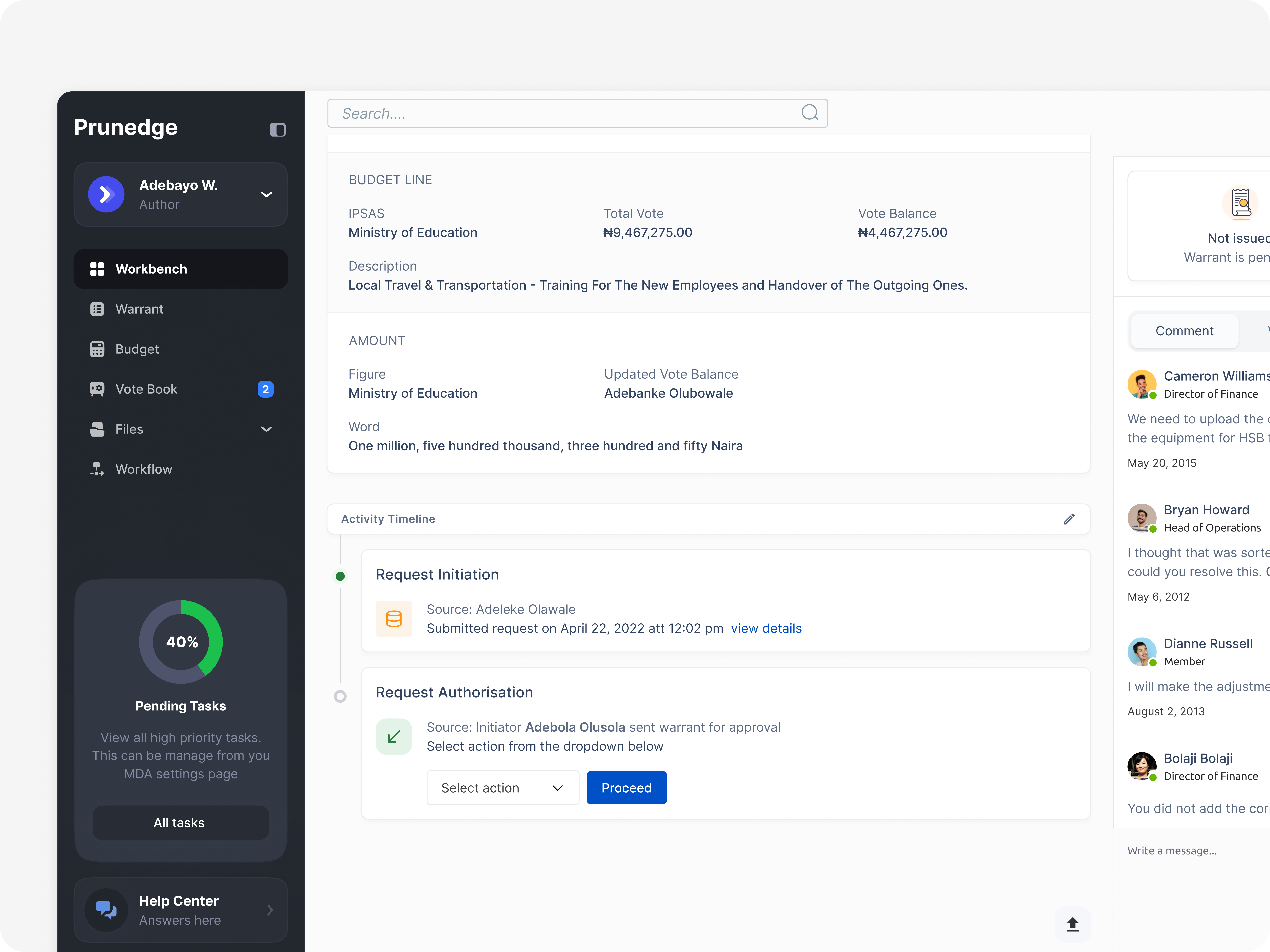
Approval Process
Process by an officer to balance the state ledger and bank statement of account for the state.

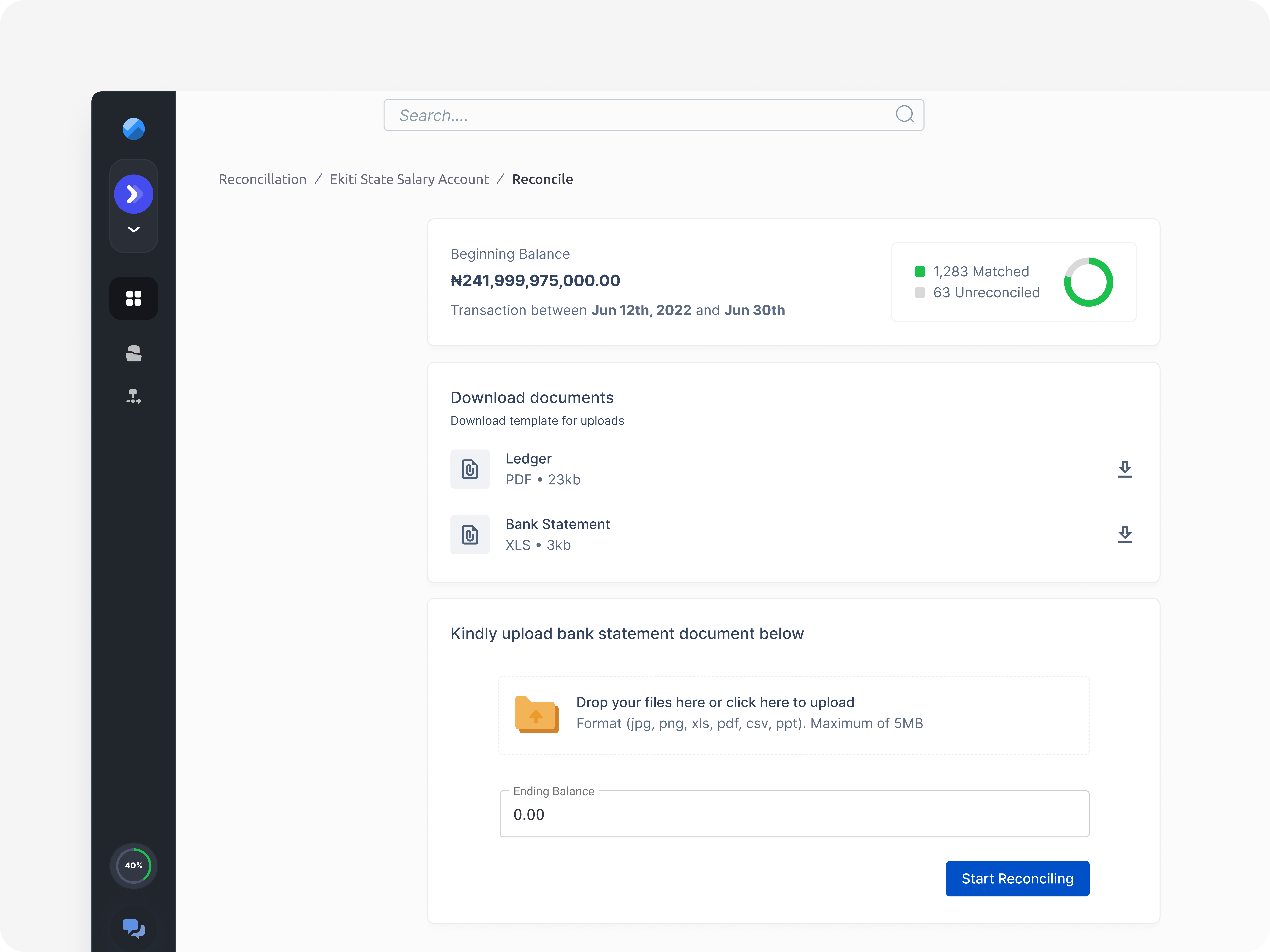
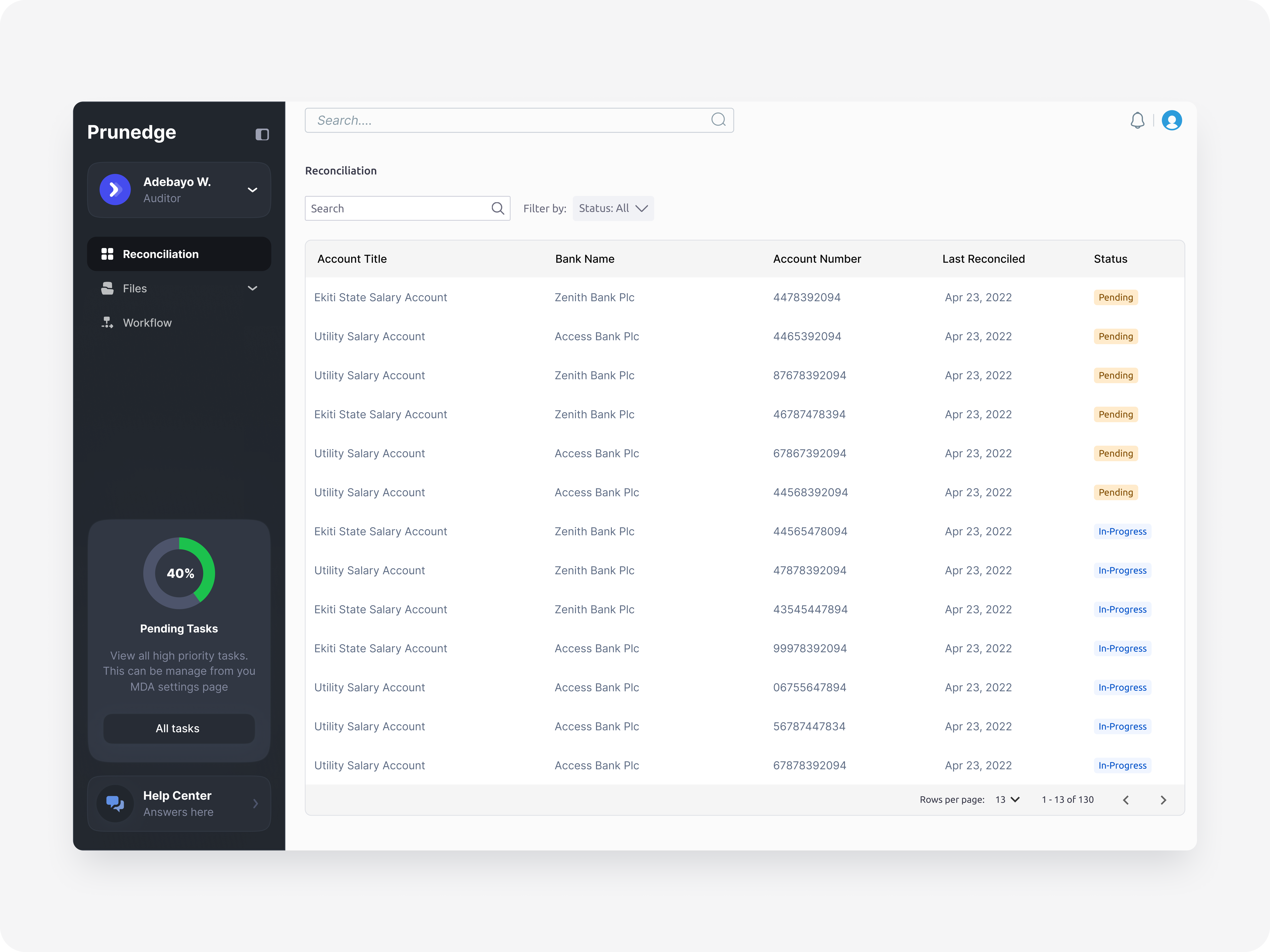
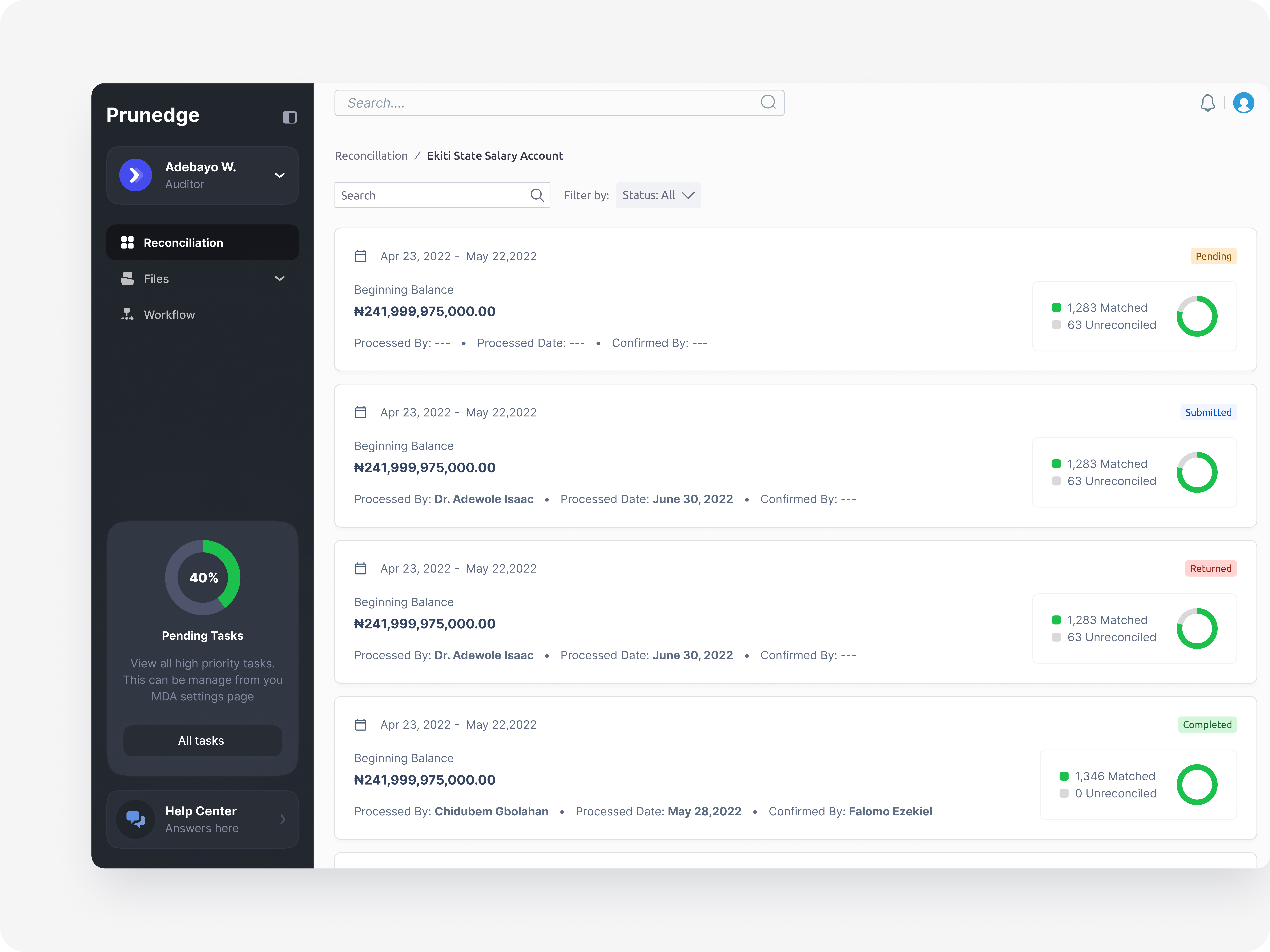
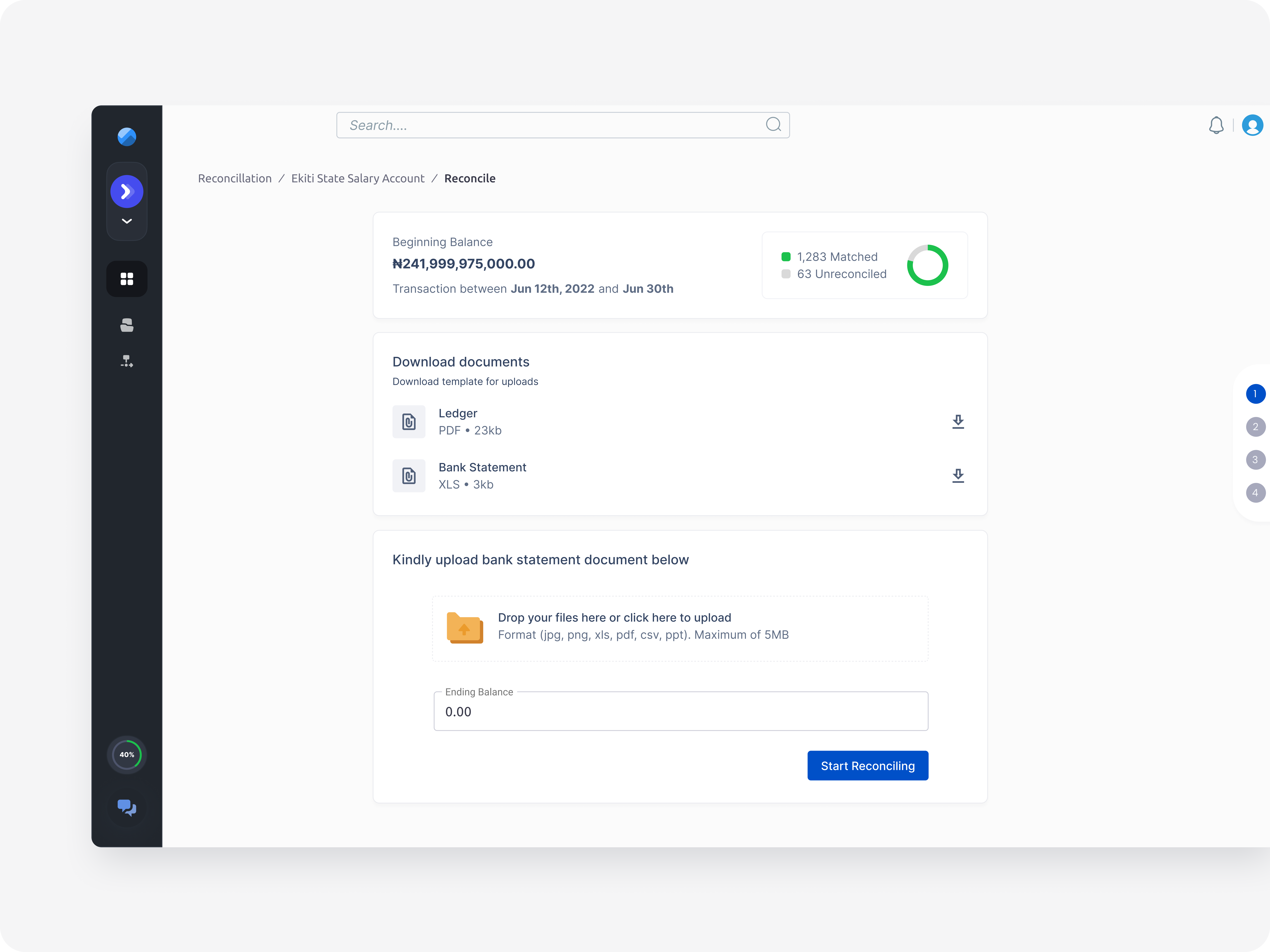
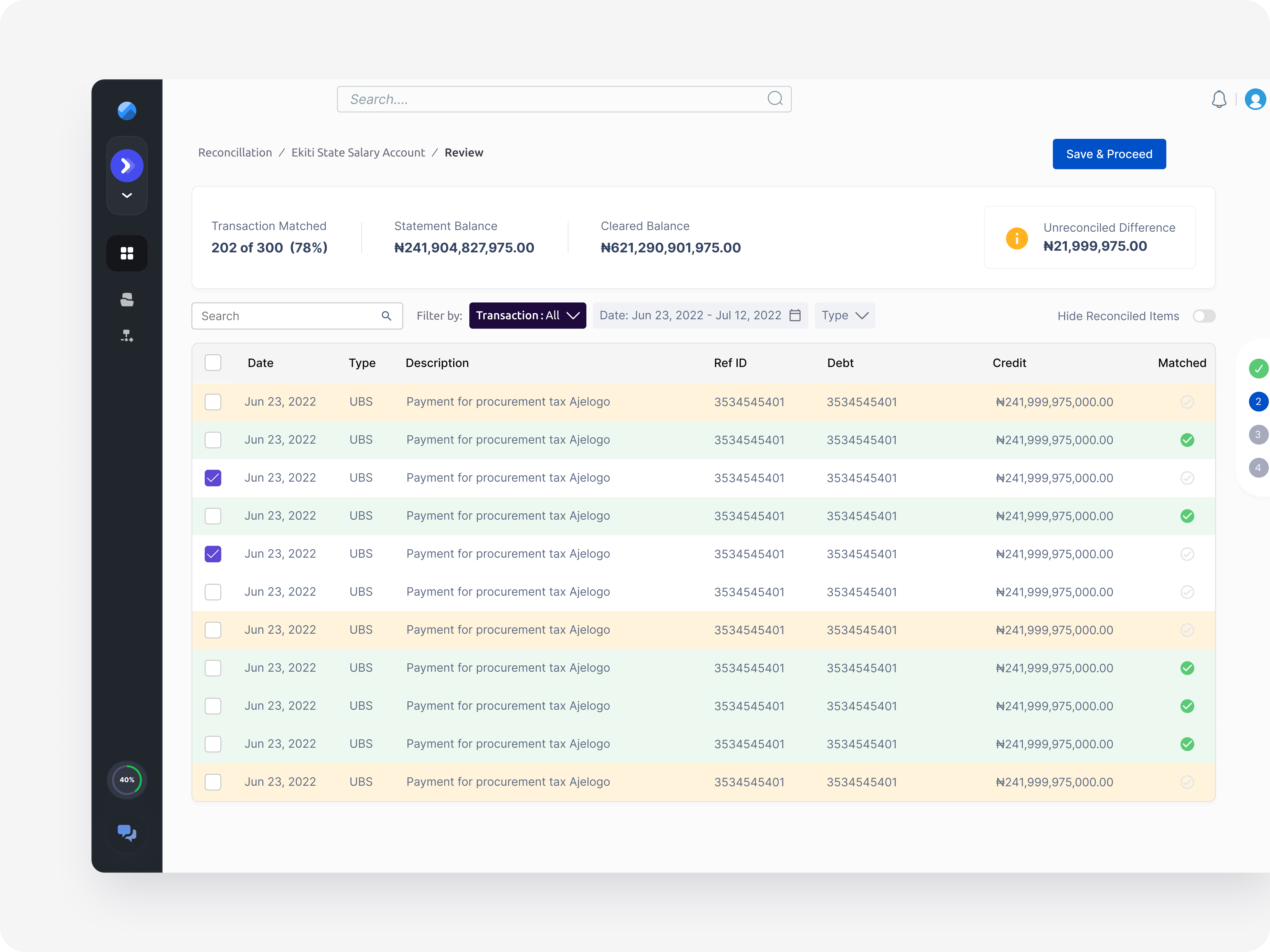
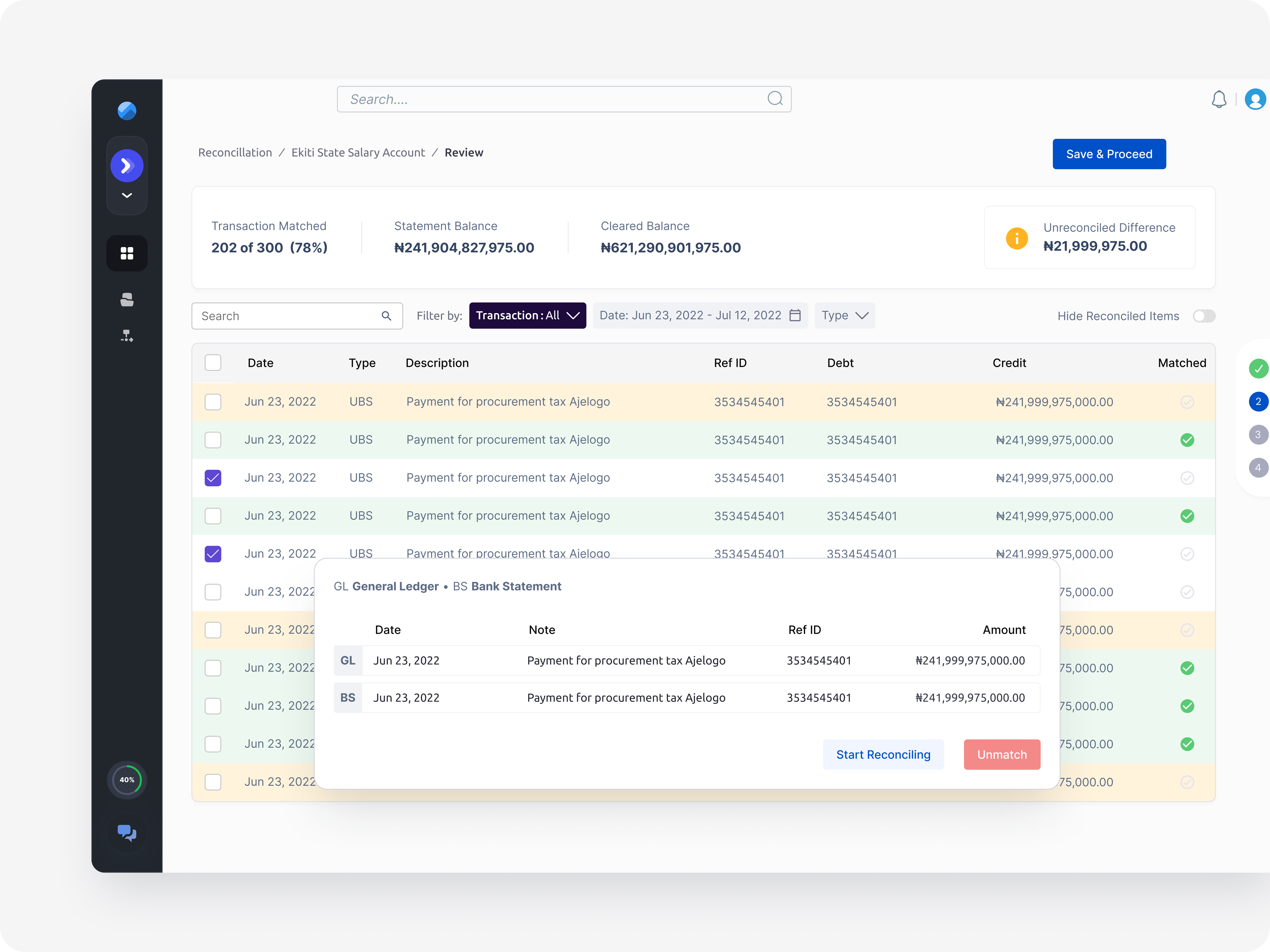
Reconcilliation Process
Process by an officer to balance the state ledger and bank statement of account for the state.

Conclusion
Design an enterprise solution that offers improved transparency and accountability in the budget and expenditure management process.
budget automation in 3 states and counting
reduction in wait time for tasks completion and feedback
in one of the states saved due to the reduction in the usage of paper and printing